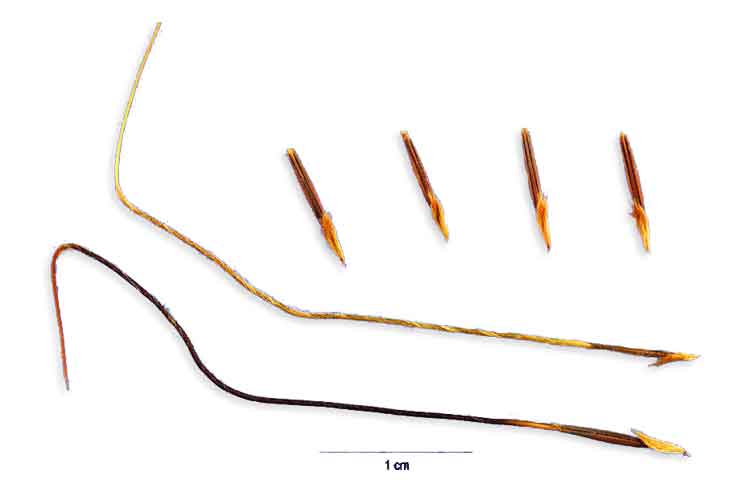
 Botanical snippet Botanical snippet
- In Australia, the species has been responsible for the elimination of the wool industry due to seeds embedding in the wool and skin of sheep, even causing deaths.
Botany
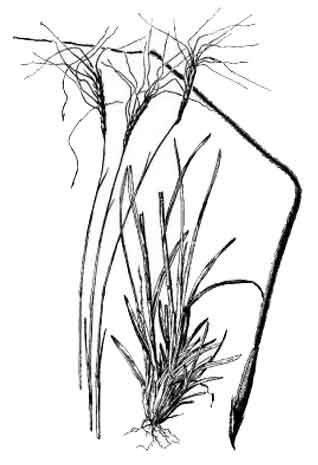
Sibat-sibatan is a tufted or somewhat scattered grass, 1 meter high or less. Stems are compressed below, simple or somewhat branched, with solitary, terminal spikes. Leaves are flat, 10 to 20 centimeters long, 4 to 7 millimeters wide. Spikes are 10 centimeters long or less, being densely imbricated and hirsute; spikelets are about 8 millimeters long, the lower few pairs staminate or neuter, the upper ones perfect. Awn of the fourth glume is stout, twisted, geniculate and about 10 centimeters long.
Distribution
- In open grasslands at low and medium altitudes, abundant in the Luzon Provinces of Ilocos Norte, La Union, Lepanto, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Viscaya, Pangasinan, Pampanga, Rizal and Zambales.
- Unquestionably introduced.
- Pantropic in distribution.
 Constituents Constituents
- Spear grass yields polysaccharides constituents: hemicellulose and cellulose. (see study below) (7)
- Nutrient composition analysis showed highest nutritive value during lush growth. Calcium in leaves and stems averaged
0.84% well in excess of the 0.2 to 0.3% in an animal diet. Phosphorus, however, averaged 0.13%, slightly less than 0.16% required. Crude protein and fat were comparable to alfalfa. (8)
- Study of leaves, stems, and inflorescence of H. contortus quantified the presence of sterols viz., stigmasterol, ß-sitosterol, campesterol, and ergosterol, with maximum contents by HPTLC of11.64 ± 0.17, 19.90 ± 0.18, and 16.64 ± 0.81 mg/g of dry wt w/w, for stigmasterol, campesterol, and ergosterol, respectively. ß-sitosterol was maximum in leaves at 56.52 ± 1.25 mg/g dry wt w/w. (17)
- Phytochemical screening of methanolic extract yielded carbohydrates, saponin, steroids, and triterpenoids, with an absence of flavonoids, alkaloids, and tannins. (9)
- NTPLC analysis of leaves, stems and inflorescence showed the maximum amount of kaempferol and quercetin is found in leaf extracts (35.80 and 17.01 mg/gm dry weight, respectively). (19)
- Chemical compositional analysis (% DM basis) yielded 92.31 dry matter %, 6.06 % crude protein, 31.15 % crude fiber, 9.74 % ash, 1.03% ether extract, and 4.68% silica.
(21)
Properties
- Awned seeds damage hides, in extreme cases penetrating to perforate the intestines.
- Studies have suggest antioxidant, mast-stabilization, anti-inflammatory,
sunscreen, broncho-relaxant activities.
Parts used
- Inflorescence, roots, various plant parts.
Uses
Folkloric
- No recorded folkloric medicinal use in the Philippines.
- Elsewhere used for dysentery, asthma, fever, myalgia, rheumatism and toothache.
- Ash of grass applied with Pongamia pinnata on piles. Paste of plant use on bites of dogs, jackals, and scorpions. For snake bites, roots are chewed or pounded and taken with water. (13)
-
The Sutos use this plant with Tribulus terestris in the treatment of rheumatism of the hands.
- In Maharashtra, India, decoction of inflorescence give three time a day as bronchodilator. (4)
- In Benin, inflorescence is an
ingredient in a decoction drunk against irritability. (11)
- In India, the Aurangabad tribe use a decoction of inflorescence as bronchodilator for asthma.
(12)
- In Ayurveda, used for eye diseases, vomiting fever, dysentery, bronchial diseases, wounds, ulcers.
(14)
- The Zulus in South Africa use the plant for treatment of burns, wounds, and rheumatism. (18)
- In the Sambhal district of Rohilkhand region of India, root paste taken orally for snake bites. (20)
Others
- Forage: A good forage grass; palatable to most livestock. Sharp awns will not develop if consistently grazed. If allowed to develop, the awn seeds will damage hides and cause injury to the intestines by perforation. Another problem as forage is the wide fluctuation of growth between rainy and dry seasons.
- Ethnoveterinary:
In Pakistan, aerial parts used as fodder for digestive disorders. (21)
- Ornamental: The interesting seed head makes it a good candidate for ornamental use.
- Crafts and House Use: Culms used as thatch for huts; commonly woven into mats and handicrafts. Â (11)
• Herbal formula: Chinese herbal formula of Heteropogon contortus, C. chinensis, S. balcalensis, and G. jasminoides used for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. (23)
Studies
• Digestibility of Polysaccharide Constituents: In a study of the digestibility of polysaccharide constituents of spear grass in bovine rumen, hemicellulose and cellulose were digested slowly and incompletely. The resistance to complete digestion in the rumen appears to be due to physical protection by lignin. (7)
• Mast Cell Stabilization / Anti-Inflammatory / Antioxidant: Study evaluated a methanolic extract of Heteropogon contortus for mast cell stabilization (in vitro anti-histaminic) and membrane stabilization (in-vitro anti-inflammatory effects. Results showed not only antioxidant activity but also membrane and mast cell stabiization. (9)
• Bronchorelaxant / Anti-Inflammatory: Study evaluated a methanolic extract of Heteropogon contortus for bronchorelaxaton (in-vitro anti-histaminic) and in vivo anti-inflammatory effects. Study showed concentraton dependent bronchorelaxant action against acetylcholine and histamine induced bronchoconstriction in tracheal muscles of guinea pig. The extract also inhibited inflammation induced by carrageenan and egg albumin. Results suggest a potential for the treatment of asthma. (10)
• Triterpenoid Lupeol / Leaves: Chromatographic evaluated the triterpenoid lupeol from methanolic extract of leaves, stem, and inflorescence of Heteropogon contortus. Results showed the present of lupeol in leaf samples at 10 mg/g of dry weight, and was absent in the other two samples. Study suggests the leaves are a good source of lupeol as alternative natural source for the synthesis of herbal drugs to control cancer and inflammation. (15)
• In Vitro Suncreen Activity / Roots: There is a demand for safe non-comedogenic, inexpensive, and efficacious plant based topical sunscreens. This study evaluated the sunscreen potential of methanolic extracts of roots of Sri Lankan grass, Heteropogon contortus. Dermatone® was used as reference agent. Results showed the root extract exhibited marked sun protection activity with SPF values of 12.85 ± 0.87, 12.80 ± 0.13, and 13.02 ± 0.03, respectively for 0.05, o.1, and 0.2 mg/mL concentration, compared to 8.21, 14.00 and 27.32 for Dermatome. The activity was attributed to flavonoids and phenols via antioxidant activity. Results suggest a safe, inexpensive, efficacious, and user-friendly sunscreen. (16)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 Botanical snippet
Botanical snippet Constituents
Constituents