
Family • Poaceae
Balili
Echinochloa stagnina (Retz.) P.Beauv.
HIPPO GRASS
| Scientific names | Common names |
| Echinochloa barbata Vanderyst | Balili (Tag.) |
| Echinochloa crus-galli var. sieberiana (Asch. & Schw.) A.Chev. | Banago (Sub.) |
| Echinochloa crus-galli var. stolonifera (Schw. &. Muschl.) A.Chev. | Lagtomna-pula (Bik.) |
| Echinochloa hostii Steven ex Link | Timsim (Tag.) |
| Echinochloa lelievrei (A.Chev.) Berhaut | Uraroi (Bik.) |
| Echinochloa malakuensis Vanderyst | Burgu grass (Engl.) |
| Echinochloa oryzetorum (A.Chev.) A.Chev. | Burgu millet (Engl.) |
| Echinochloa scabra (Lam.) Roem. & Schult. | Hippo grass (Engl.) |
| Echinochloa stagnina (Retz.) P.Beauv. | Long-awn water grass (Engl.) |
| Oplismenus scaber (Lam.) Kunth | |
| Oplismenus stagninus (Retz.) Kunth | |
| Orthopogon stagninus (Retz.) Spreng. | |
| Panicum burgu A.Chev. | |
| Panicum crus-galli var. leopstachyum Franch. | |
| Panicum crus-galli var. maximum Franch | |
| Panicum crus-galli var. sieberianum Asch. & Schweinf. | |
| Panicum crus-galli var. stagninum (Retz.) Trimen | |
| Panicum crus-galli var. setoloniferum Schweinf. & Muschl. | |
| Panicum crus-galli var. submuticum Franch. | |
| Panicum galli Thunb. | |
| Panicum lelievrei A.Chev. | |
| Panicum oryzetorum A.Chev. | |
| Panicum oryzetum A.Chev. | |
| Panicum scabrum Lam. | |
| Panicum scabrum subsp. burgu (A.Chev.) A.Chev. | |
| Panicum scabrum var. franchetii A.Chev. | |
| Panicum scabrum var. leiostachyum (Franch.) A.Chev. | |
| Panicum scabrum subsp. lelievrei A.Chev. | |
| Panicum scabrum subsp. oryzetorum A.Chev. | |
| Panicum scabrum var.submuticum (Franch.) A.Chev. | |
| Panicum scabrum var. stagninum (Retz.) A.Chev. | |
| Panicum sieberianum (Asch. & Schweinf.) Sickenb. | |
| Panicum stagninum Retz. | |
| Panicum subaristatum Peter | |
| Balili is a common names shared by Panicum stagnimum and Juncus effiusus, Pingot (Bon.) | |
| Panicum stagninum Retz. is a synonym of Echinochloa stagnina (Retz.) P.Beauv. | |
| Echinochloa stagnina (Retz.) P.Beauv. is an accepted species. KEW: Plants of the World Online | |
| Other vernacular names |
| CAMEROON: Bourboumdje. |
| FIJIAN: Bangara gaddi. |
| FRENCH: Borgou, Pied de coq du Niger, Roseau sucré, Roseau a miel du Niger. |
| HAUSA: Bonekouan, Buuru(u)gu, Sakera.s |
| INDONESIAN: Rumput kumpai. |
| PORTUGUESE: Capim arroz. |
| SWEDISH: Borstig honshirs. |
Botany Distribution
Properties Studies Availability |
| Abuse and Plagiarism of the Compilation on Philippine Medicinal Plants Under the Guise of Fair Use |
Updated August 2023 / February 2020 / June 2017 / October 2015
![]()
 |
PHOTOS / ILLUSTRATIONS |
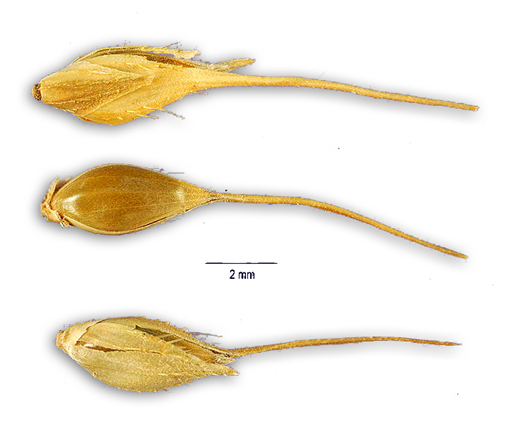
| IMAGE SOURCE: Seeds /Echinochloa stagnina (Retz.) P. Beauv. - hippo grass / ECST4 / Jose Hernandez, hosted by the USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / USDA |
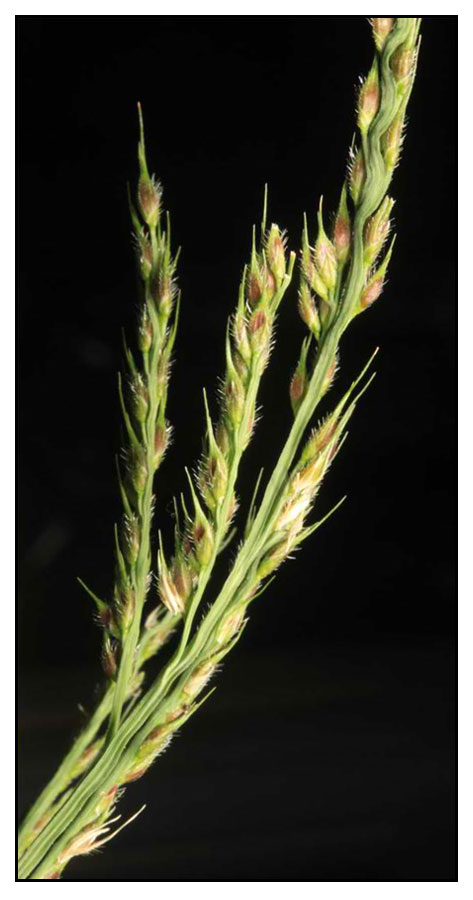
| IMAGE SOURCE: Photograph / Echinochloa stagnina - Fruiting stem / Tariq Stevart / Creative Commons / click on image to go to source page / Useful Tropical Plants |
| IMAGE SOURCE: Illustration / Echinochloa stagnina (Retz.) P. Beauv. [as Panicum stagninum Retz.] Wood, J.M., Evans, M.S., Natal plants, vol. 5: t. 492 (1904-1908) / Plant Illustrations |
Additional
Sources and Suggested Readings |
• |
DOI: It is not uncommon for links on studies/sources to change. Copying and pasting the information on the search window or using the DOI (if available) will often redirect to the new link page. (Citing and Using a (DOI) Digital Object Identifier) |
| List of Understudied Philippine Medicinal Plants |
• |
 |

 Constituents
Constituents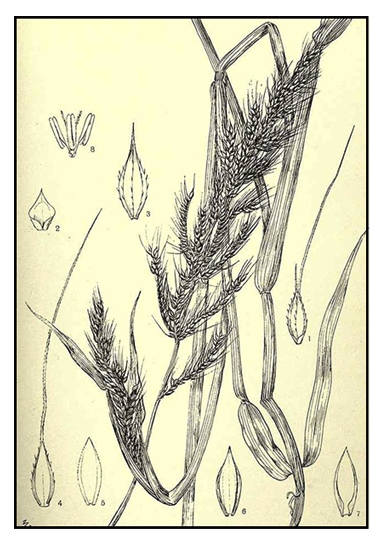 Uses
Uses 