 Gen info Gen info
• The winged bean belongs to the genus Psophocarpus of the legume family, Fabaceae. (23)
• Sometimes called "poor man's food" as the leaves, flowers, roots, and pods are all edible, eaten raw or cooked.
• Etymology: The genus name Psophocarpus means "noisy fruit", referring to some plants in the genus that make a popping noise when they dehisce and release the seeds. The tetra from the specific epithet tetragonolobus mean "four", referring to the four sides of the fruit. (26)
Botany
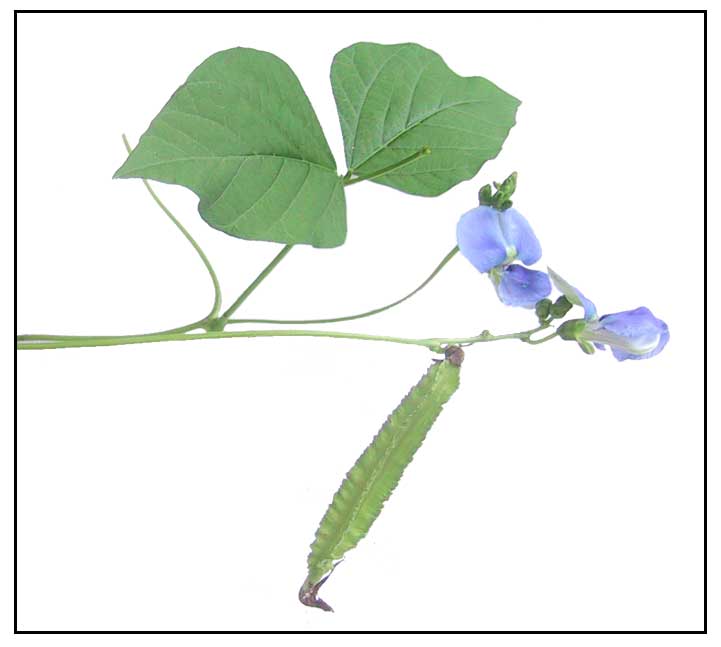
• Sigarilyas is a vine with climbing stems
and leaves, to a height of 3-4 meters. Leaves are pinnate or palmate
to trifoliate. Bean pod is about 6 to 8 inches long, four-angled. Flowers
are large and pale to bright blue.
 • Winged bean plant grows as a vine with climbing stems and leaves, 3–4 m (10–13 ft) in height. It is an herbaceous perennial, but can be grown as an annual. It is generally taller and notably larger than the common bean. Leaves can be 15 cm (6 in) long. Leaf shape ranges from ovate to deltoid, ovate-lanceolate, lanceolate, and long lanceolate; the green tone of the leaves also varies. Stem is most commonly green, but sometimes boasts purple. Flower is large and pale blue. Bean pod may be smooth or rough, depending on the genotype, typically 15–22 cm (6–8+1⁄2 in) long, rectangular in cross-section (though sometimes appearing flat), and has four wings with frilly edges running lengthwise. Skin is waxy and the flesh partially translucent in the young pods. Color of the pods may be cream, green, pink, or purple. When fully ripe, the pod turns an ash-brown colour and splits open to release the seeds (beans). Seed shape is often round; oval and rectangular seeds also occur. Seeds may appear white, cream, dark tan, or brown, depending on growing and storage conditions. (22) • Winged bean plant grows as a vine with climbing stems and leaves, 3–4 m (10–13 ft) in height. It is an herbaceous perennial, but can be grown as an annual. It is generally taller and notably larger than the common bean. Leaves can be 15 cm (6 in) long. Leaf shape ranges from ovate to deltoid, ovate-lanceolate, lanceolate, and long lanceolate; the green tone of the leaves also varies. Stem is most commonly green, but sometimes boasts purple. Flower is large and pale blue. Bean pod may be smooth or rough, depending on the genotype, typically 15–22 cm (6–8+1⁄2 in) long, rectangular in cross-section (though sometimes appearing flat), and has four wings with frilly edges running lengthwise. Skin is waxy and the flesh partially translucent in the young pods. Color of the pods may be cream, green, pink, or purple. When fully ripe, the pod turns an ash-brown colour and splits open to release the seeds (beans). Seed shape is often round; oval and rectangular seeds also occur. Seeds may appear white, cream, dark tan, or brown, depending on growing and storage conditions. (22)
• Growth form: Herbaceous climber that grows 3 - 4 m in height. Foliage: Leaves green and trifoliate (compound leaves each consisting of 3 leaflets). Leaflets large (8 – 15 cm long, 8 - 15 cm wide at the broadest point) and ovate (lateral leaflets) or deltoid (terminal leaflet). Flowers: Pea-like flowers classified as papilionaceous are usually light blue, but occasionally white (2.5 - 3.5 cm wide). Fruits: Fruits are elongated pods (15 - 30 cm long, 3 cm wide) and square or rectangular in cross-section. Frilly or sometimes smooth wings protrude along the length of the pod at each corner. At maturity, pods break open to release 5 - 21 approximately round, smooth seeds. (26)
 Distribution Distribution
- Introduced, naturalized.
-
Cultivated, semi-cultivated, and occasionally spontaneous or subspontaneous in most parts of the Philippines at low and medium elevation. (21)
- Native to Tanzania.
Constituents
- Rich in oil (up to 17%), protein, vitamin E and calcium.
- Proximate analysis showed P. tetragonolobus to be rich in proteins (33.83%), with considerably high amount of carbohydrate (22.30%). Fat content was 17.51%; crude fiber, 12.23%; water content, P>0.05. (see study below) (6)
- Mineral composition (mg/kg) of winged beans yielded magnesium, 2238.18 ±0.04; zinc, 364.76 ±0.64; copper, 90.79 ±0.72; calcium, 889.86 ±0.63, sodium, 1972.34 ± 0.69; potassium, 4219.30 ± 0.81. (6)
 - Study showed that fatty oil from fully mature seeds had a higher proportion of unsaturated fatty acids (75.5%); immature seeds yielded a higher percentage of saturated FA (61.3%). Unsaponification of fatty oil yielded stigmasterol (66.4%) and ß-sitosterol (25.1%). Total lipids of fully mature seeds yielded neutral, glyco- and phospholipids. Fatty oil of fully mature seeds yielded mono-saturated FA (38.6%) and polyunsaturated FA (36.9%) without trans-fatty acids, thereby meeting the edible oil standard.
(10) - Study showed that fatty oil from fully mature seeds had a higher proportion of unsaturated fatty acids (75.5%); immature seeds yielded a higher percentage of saturated FA (61.3%). Unsaponification of fatty oil yielded stigmasterol (66.4%) and ß-sitosterol (25.1%). Total lipids of fully mature seeds yielded neutral, glyco- and phospholipids. Fatty oil of fully mature seeds yielded mono-saturated FA (38.6%) and polyunsaturated FA (36.9%) without trans-fatty acids, thereby meeting the edible oil standard.
(10)
- Nutritional analysis of raw immature seeds per 100 g. yielded: (1) Principle: energy
49 Kcal, carbohydrate 4.31g, protein 6.95g, total fat 0.87g, cholesterol 0 mg; (2) Vitamins: folates 66 µg, niacin 0.900 mg, pantothenic acid 0.059 mg, pyridoxine 0.113 mg, riboflavin 0.100 mg, thiamin 0.140 mg, vitamin A 128 IU, vitamin C 18.3 mg; (3) Electrolytes: sodium 4 mg, potassium 240 mg; and (5) Minerals: calcium 84 mg, copper 0.051 µg, iron 1.5 mg, magnesium 34 mg, manganese 0.218 mg, phosphorus 37 mg, selenium 1.5 µg, zinc 0.39 mg. (13)
- Nutritional values of raw, mature seeds of winged beans per 100 g(3.5oz): Energy 1,711 kJ (409 kcal); Carbohydrates 41.7 g, Dietary fiber 25.9g; Fat 16.3 g, saturated 2.3 g, monosaturated 6 g, polyunsaturated 4.3 g; Protein 29.65 g; Vitamins: Vitamin A 0 IU, Thiamine (B1) 1.03 mg, Riboflavin (B2) 0.45 mg, Niacin (B3) 3.09 mg, Pantothenic acid (B5) 0.795 mg, Vitamin B6 0.175 mg, Folate (B9) 45 µg, Vitamin C 0 mg; Minerals: Calcium 440 mg, Iron 13.44 mg, Magnesium 179 mg, Manganese 3.721 mg, Phosphorus 451 mg, Potassium 977 mg, Sodium 38 mg, Ziinc 4.48 mg. (USDA Database) (23)
- Winged bean contains many anti-nutritional factors: trypsin inhibitors, chymotrypsin inhibitors (WCI), hemagglutinins, amylase inhibitors, phytates, phytic acid, flatulence factors, hydrogen cyanide, saponins, tannins, and other phenolic compounds.
(see study below) (24)
Properties
- Studies have suggested antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive, antioxidant, anti-candidal, platelet aggregation inhibitory, hepatoprotective, anthelmintic, phytostimulatory properties.
Uses
Edibility
- Whole plant is edible,
the beans used as vegetable; but the other parts –leaves, flowers
and roots–are also edible. Immature seeds used in soups.
- Young pods can be eaten raw or added to salads.
- Tender pods, the most widely eaten part of the plant, are best before they exceed 2.5 cm (1 in) in length.
(23)
-
Flowers used as rice and pastry colorant; eaten raw or cooked; a sweet flavor that makes an appealing addition to salads.
- Young leaves can be pickled or prepared as vegetable, like spinach.
- Leaves and young shoots, raw or cooked, are surprisingly delicious.
- Seeds are about 35% protein and 18% fat, and requires cooking for 2 - 3 hours to destroy trypsin inhibitors and hemagglutinins that inhibit digestion. They can be eaten dried or roasted Dried or ground seeds can make a useful flour, and brewed as substitute to coffee beans. (23)
- Good source of vitamins A and C, calcium and iron.
- Roasted seed used as coffee substitute.
Folkloric
- No reported folkloric medicinal use
in the Philippines.
Others
- Agroforestry: Winged bean is an effective cover crop. Uniform with the ground, it suppresses weed growth. As a restorative crop, it can improved nutrient-poor soil with nitrogen when it is turned over into the soil. (22)
- Fodder: A potential food source for ruminants, poultry, fish, and other livestock. In Papua New Guinea, the husks are fed to domesticated pigs as dietary supplement. (23)
- Oil: Oil can be extracted from the seeds, and used for cooking and frying.
- Colorant: Flowers used to color food products, like rice and pastries.
Studies
• Antimicrobial / Pods / Leaves:
Results of study of extract of PT pods showed activity against B. subtilis
and B. cereus, P mirabilis, E coli, S typhi, K pneumonia and C albicans
and suggested a potential source for antimicrobial compounds. (1) Methanol extract of Psophocarpus tetragonologus leaves exhibited
bactericidal effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa.(3) Study of a methanol extract of P. tetragonolobus leaves for antimicrobial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa showed favorable activity with MIC of 2.55 mg/mL. SEM studies showed complete collapse of the bacterial cells. The extract exhibited no significant toxicity (LC50=1.30 mg/mL) against Artemia salina. (15)
• Fungicidal: Study of methanol
extract of PT root showed no toxicity and a favorable antimicrobial
activity against Candida albicans. (2)
• Aluminum Content of Edible Portion: Study was done to evaluate the accumulation of aluminum in the edible parts of the plant: leaves, pods, seeds and tubers. Results showed all edible portions of the plant accumulate aluminum from high to very high levels compared to an average of less than 300 ppm in other crop plants; the accumulation was highest in the youngest tissues, especially the roots, recording as high as 25,000 ppm. (4)
• Phytohemagglutinins / Seeds: One of the drawbacks in the utilization of winged bean protein is the presence of anti-nutritional factors typical of legumes. Study evaluated the seeds from eleven cultivars of Psophocarpus tetragonolobus for phytohemagglutinin activity. Levels ranges from 3,200 to 25,600 hemagglutinating units/g sample, on a fresh weight basis. Seeds showed greater activity than tubers and leaves. Phytohemagglutinins were found to be thermolabile. (5)
• Proximate Analysis: Winged beans is unique among leguminous crops in that many plant parts—leaves, pods, seeds, and tubers—are edible and rich in protein. Based on findings on proximate analysis, winged beans could be useful in the formulation of infant formula. (see constituents above) (6)
• Isolectins / Leaves: Study isolated two isolectins from the leaves of winged bean, differing from each other in immunological properties, hemagglutinating activities, sugar inhibition patterns, and amino aid compositions. (7)
• Anti-Candidal / Pod Extract: Study evaluated a pod extract of Psophocarpus tetragonolobus for antimicrobial activity against Candida albicans. Results showed alteration in morphology and complete collapse of yeast cells after 36 hours of exposure. Study confirms the possible antimicrobial potential of the pod extract. (8)
• Anti-Inflammatory / Antioxidant / Anti-Nociceptive: Study evaluated the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-nociceptive properties of six Malaysian medicinal plants, including Psophocarpus tetragonolobus. All plants showed significant nitric oxide inhibitory activity without causing cytotoxicity to RAW 264.7 cells. All plants showed different degrees of antioxidant activities, attributed to phenolic compounds. All plant species suppressed writhing response of mice at different degrees of inhibition. (9)
• Hepatoprotective / Seeds: Study evaluated the hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of total flavonoids from P. tetragonolobus seeds in vitro and in vivo in carbon tetrachloride induced acute liver injury in mice. Results showed significant hepatoprotective effect, possibly by scavenging of free radicals and inhibition of lipid peroxidation and TNF-α expression. (14)
• Antibacterial / Leaves:Study of a methanol extract of P. tetragonolobus leaves for antimicrobial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa showed favorable activity with MIC of 2.55 mg/mL. SEM studies showed complete collapse of the bacterial cells. The extract exhibited no significant toxicity (LC50=1.30 mg/mL) against Artemia salina. (15)
• Platelet Aggregation Inhibition Activity / Pod: Study evaluated the antiplatelet activity of pods of P. tetragonolobus in vitro. A 4mg/mL concentration showed the highest average percent platelet aggregation inhibition of 69.58% and greatest average percent antiplatelet activity of 75.49% among the pod extracts. (16)
• Biodiesel Potential / Seed Oil: Paper presents preliminary studies on biodiesel from two novel sources of oil: fruit pulp of C. ovatum (pili) and seed of P. tetragonolobus (winged bean). The kinematic viscosity of the FAME from sigarilyas was above maximum limit for Philippine standard. Initial results suggest acceptable FAME may be obtained from these two new potential sources of feedstocks. (17)
• Effect on Heat Treatment on Nutritional value of winged bean: Autoclaving suggested that autoclaving at 124 c within minutes should be adequate to remove protease inhibitors and can improved digestibility of winged beans. (18)
• Anti-Nutritional Factors: Winged bean contains many anti-nutritional factors: trypsin inhibitors, chymotrypsin inhibitors (WCI), hemagglutinins, amylase inhibitors, phytates, phytic acid, flatulence factors, hydrogen cyanide, saponins, tannins, and other phenolic compounds. Hemagglutinins along with trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitors are destroyed by heat, so only raw seeds will contain these anti-nutritive factors. Autoclaving will also decrease the activity of all three; after autoclaving the flour for 30 min, the activities of all three components are abolished. The amount of tannins and phytates, similar in amounts present in soy beans, are not very high and not harmful. Despite the antinutrients, the positive nutritional benefits offered by winged bean makes it a potential functional ingredient in various food formulations. (24)
• Antioxidant / Anti-Inflammatory: Study evaluated P. tetragonolobus extracts for antioxidant and anti-infllammatory effects in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Both extracts were right in bioactive molecules and exerted substantial antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Extract treatment in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells resulted in significant downregulation of expressions of TNFα, IL-6, IL-1ß mRNA, along with attenuation of inducible iNOS and COX-2 protein expression. Results suggest potential for treatment of diseases related to oxidative stress and inflammatory reactions. (25)
• Effects on Cooking on Antinutrients and Antioxidant Properties: Antinutrient concentrations were determined using standard methods and antioxidant activity by DPPH assay. Five different varieties were studied. Phytate, cyanogenic glycosides and tannin levels were significantly (p<0.05) reduced by cooking. Tannin was significantly lower in a cooked sample compared to raw sample. Phenolic content was significantly (p<0.05) increased in one variety due to cooking. There was no significant difference in antioxidant activity between raw and cooked samples across the five varieties. (27)
• Anthelmintic / Leaves: Study evaluated the anthelmintic activity of mature green leaves extract of Psophocarpus tetragonolobus against earthworm Pheretima posthuma. Screening for primary and secondary metabolites yielded carbohydrates, diterpenes, triterpenes, saponins, and phenolic compounds. Results showed anthelmintic activity evidenced by wriggling movements in 6-7 minutes with 5 mg/ml of extract, and curling movements after 3-4 minutes with 10 mg/ml extract. Elongation was observed with 40 mg/ml of plant extract. Time for paralysis was concentration dependent. (28)
• Silver Nanoparticles / Phytostimulatory / Leaves: Study reports on the simple, cost-effective, and eco-friendly synthesis of capped AgNPs using P. tetragonolobus leaf extract. FTIR confirmed the presence of polyphenols and an aromatic group of protein that played an important role in the reduction of AgNO3. AgNPs can enhance antioxidant enzymes peroxidase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, SOD, and a higher concentration of soluble sugar, soluble protein, sucrose and chlorophyll contents to support seedling growth. It was concluded that AgNPs50 was the best nanopriming treatment to enhance the germinability, antioxidant enzymes, and biochemical activities in P. tetragonolobus. (29)
Availability
Cultivated. |


![]()

