 Gen info Gen info
- Clausena is a genus of flowering plants in the citrus family, Rutaceae. It was first identified by Dutch botanist Nicolaas Laurens Burman in 1768. (16)
- Clausena was named for Norwegian clergyman Peder Clausson Friis (1545-1614), the translator of the Icelandic historian and poet, Snorri Sturluson.
(16)
-
Clausena anisum-olens was studied in Indonesia around World War II under the name Clausena anisata Hook.f. The rutaceous tree whose leaves contain an essential oil of almost pure anethole is identified as a cultivar of the Philippine species Clausena anisum-olens (Blanco) Merr. The origin of the cv. can be traced back to 1820, when French botanist Perrottet collected it from Manila and brought them back to Paris via La Réunion. (15)
Botany
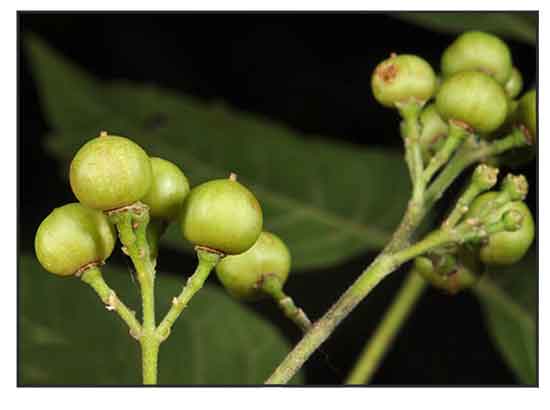
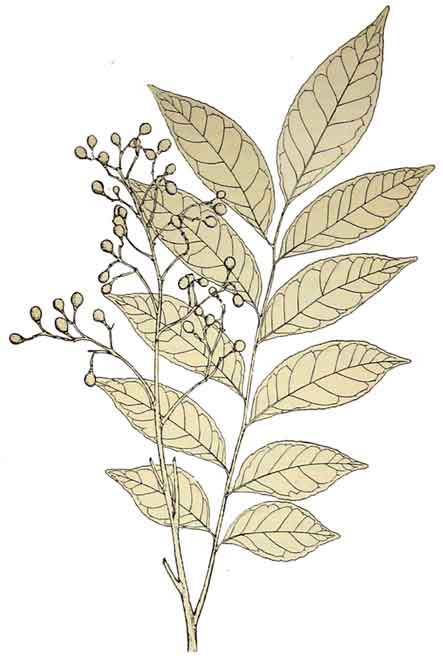
Kayumanis is a small tree up to 3 to 6 meters in height. Leaves are 20 to 30 centimeters long, with 7 to 11 leaflets which are ovate-lanceolate to lanceolate, 5 to 11 centimeters long. Panicles are 15 to 20 centimeters long, terminal, and in the upper axils. Flowers are greenish, white, fragrant, 5-parted, about 8 millimeters in diameter. Fruit is nearly spherical or ovoid, about 1 centimeter in diameter, whitish when mature.
Distribution
- Native to the Philippines.
-
In forests, at low and medium altitudes, in Bontoc, Benguet, Pampanga, Batangas, Bataan, Laguna, Rizal, and Sorsogon Provinces in Luzon; and in Masbate, Basilan and Mindanao, ascending to 1,500 meters.
- Also native to Borneo and Taiwan.
- Introduced and reportedly naturalized in China.
 Constituents Constituents
- Distillation of the leaves yield a colorless oil with a faint odor of anise or anethol.
- The volatile oil contains methyl clavicol.
- The chemical composition of the oil varies among individual plants, from almost pure methyl chavicol (estragol) to almost pure anethol. A minor component is anisaldelhyde.
- Analysis of aqueous extract yielded tannins and saponins.
- Study isolated a new cyclopeptide, clausenain.
- Essential oils from stems roots, leaves, fruits, and flowers yielded 4-methoxy-6-(2-propenyl)-1,3-benzodioxole. The main types of the compounds are aromatic hydrocarbons, alkane, olefin and fatty acids. (9)
- 100 kg. of fresh leaves yield 1.6 - 2 kg of oil. One ha estimates a possible essential oil yield of 350-750 kg per year.
- Study of fruits isolated 18 carbazole alkaloids (1-18), containing three new ones, clausenanisines A-C (1-3), and three new naturally occurring carbazome alkaloids, clausenanisines D-F (4-6), and 12 known analogues (7-18). (see study below) (18)
Properties
- Leaves when crushed are aromatic.
- Alcoholic extracts have a strong anise-like odor.
- Oil extracted from the leaves is inactive, with a faint odor of anise or anethol.
- Study suggests hepatoprotective and antimicrobial, antifungal, insecticidal, PTPB1 and α-glucosidase inhibitory, antimicrobial, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, repellent properties.
 Parts used Parts used
Roots, leaves and fruits.
Uses
Edibility
- Leaves used as a condiment in preparing local dishes and beverages.
- Essential oil from the leaves considered a potential substitute of anise oil for the making of "anisado," a local alcoholic beverage.
- Fruits are edible. Fresh ripe fruits are extremely popular seasonal fruits in south China.
Folkloric
- In the Philippines, decoction of roots and fruits used for cough with fever.
- Decoction of leaves used for nausea of pregnancy.
- Leaves are stuffed in pillows for its soporofic effect.
- Leaves used in baths for rheumatism.
- In China, the leaves and twigs are used for the treatment of dysentery and arthritis.
Others
- Cigarette flavoring: Leaves also used to flavor cigarettes.
- Oil: Essential oil is a potential cheap source of natural anethol.
Studies
• Monoterpenoid Coumarins / Antifungal: Study isolated two new monoterpenoid coumarins: anisucumarin A and B. The EtOH extract of Clausena anisum-olens showed antifungal activity against C. albicans, C. tropicalis and C. krusei. Anisucumarin A and B failed to show detectable antifungal activity. (1)
• Octapeptide: Study isolated a new cyclic octapeptide, clausenain B, a phenylalanin-rich cyclic octapeptide. (2)
• Hekumarone: Study isolated a new O-terpenoidal coumarin, hekumarone, from the leaves and twigs. Coumarins are considered characteristic and distinguishable chemical markers for the Rutaceae family. (4)
• Insecticidal / Anisaldehyde: Anisaldehyde, a compound found in the essential oil of Clausena anisum-olens was tested for insecticidal activities against Acanthoscelides obtectus and Callosobruchus maculatus. It caused significant mortality in the two tested insects, the latter more susceptible than the former. (3)
• Antimicrobial: Study extracted a volatile oil from the nutlets of Clausena anisum-olenas. The major chemical compositions were 4-methoxy-6-(2-propenyl)-1,3- benzodioxole (47.07%), 1,2,3-trimethoxy-5-(2-propenyl)- benzene (8.25%), 2,6- dimethoxy-4-(2-propenyl)-pheno (7.17%), n-hexadecanoic acid (7.05%) and tricosane (4.95%). The volatile oil had strong inhibitory effect against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus cereus. (8)
• Choleretic / Hepatoprotective / Leaves: A previous study showed an ethanolic extract to possess a choleretic effect in mice. This study showed an ethyl acetate fraction with the highest choleretic and hepatoprotective effect in mice, inhibiting the increase of ALT, AST, and bilirubin levels. (12)
• Leaf Essential Oil / Variations and Genetic Origins: In a study of 91 cultivated and wild plants, main compounds of the oil were (E)-anethole and/or methyl chavicol, with respective percentages stable through time and cultivation. Variations in oil content showed three chemovariants: pure anethole oil, pure methyl chavicol oil, and mixed oil (about 90% anethole and 10% methyl chavicol). (13)
• Hypocholesterolemic / Leaves: Study evaluated the effects of ethanol extract of C. anisum-olens leaves on cholesterol level of Triton-X induced female Sprague-Dawley rats. Acute oral toxicity using OECD 425 guidelines showed the crude extract was nontoxic up to 2000 mg/kg. Lipid-lowering assay showed reduction of serum cholesterol (87.21 mg/dL), triglycerides (58.09 mg/dL), and LDL (27.82 mg/dL) for the 200 mg/kw extract. Results was comparable to atorvastatin which showed serum cholesterol reduction of 80.90 mg/dL, triglycerides 55.94 mg/dL, and LDL 22.09 mg/dL. (14)
• Anisucoumaramide / MAO-B Isoenzyme Inhibitory Activity: Study isolated a new coumarin, anisucoumaramide (1), and a new δ -truxinate derivative, anisumic acid (2). Compound 1 showed high selectivity for the MAO-B isoenzyme and inhibitory activity in the nanomolar range. Putative biosynthesis pathways toward 1 and 2 were proposed. (17)
• Carbazole Alkaloids / Potential PTP1B and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity / Fruits: Study of fruits isolated 18 carbazole alkaloids (1-18), containing three new ones, clausenanisines A-C (1-3), and three new naturally occurring carbazome alkaloids, clausenanisines D-F (4-6), and 12 known analogues (7-18). Compounds 1-18 exhibited remarkable PTP1B inhibitory activities with IC50s in range of 0.58 to 38.48 µM. Compounds 1-18 also showed significant α-glucosidase inhibitory activities with IC50s from 3.28 to 192.23 µM. Results suggest potential for developing new PTP1B inhibitors and α-glucosidase inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. (18)
• Toxicity and Repellency Against Two Stored Product Insects / Essential Oil: The essential oil of C. anisum-olens showed strong contact toxicity and repellency against Lasioderma serricorne and Liposcelis bostrychophila adults. Hydrodistillation and GC-MS analysis revealed main components of the EO were myristicin (36.87%), terpinolene (13.26%), p-cymene-8-ol (12.38%), and 3-carene (3.88%). Myristicin and p-cymene-8-ol showed strong contact toxicity against L. serricorne (LD50 18.96 and 39.68 µg per adult) and L. bostrychohila (LD50 20.41 and 35.66 µg per adult). Myristicin and p-cymene-8-ol showed strong repellent toxicity to Li. bostrychophila. (19)
Availability
Wild-crafted. |

![]()





 Parts used
Parts used 