|

Gen info
- Epipremnum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. They are evergreen perennial vines climbing with the aid of aerial roots.
-
All plants of the genus Epipremnum are considered toxic, mostly due to the presence of trichosclereids (long sharp cells) and raphides. Plants are commonly grown as houseplants in temperate regions are known as centipede tongavine, pothos or devil's ivy.
-
Etymology: The genus name Epipremnum derives from Greek terms epi (upon) and premna (tree stump), referring to the epiphytic growth habit of the plants in the genus. The species epithet pinnatum refers to the pinnately-lobed shape of mature leaves.
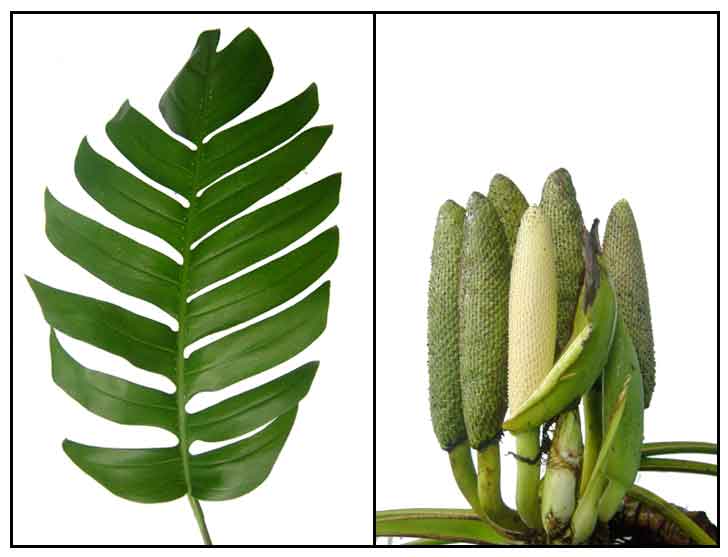
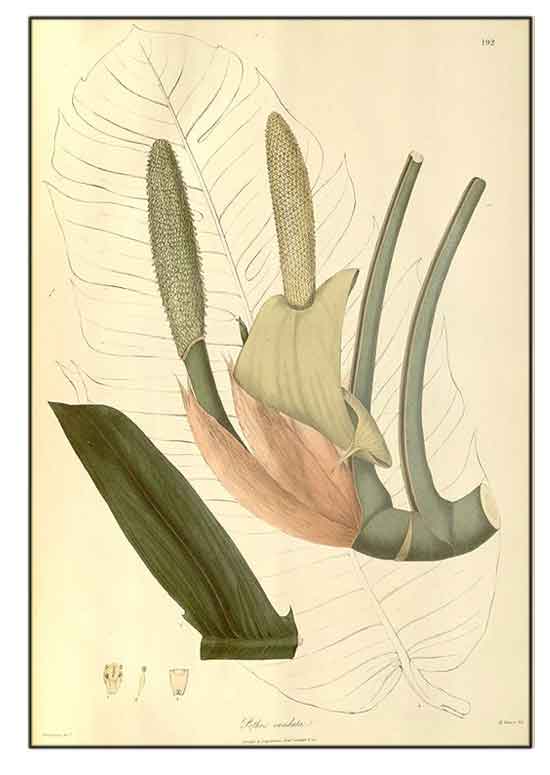
 Botany Botany
Tibatib is a stout vine climbing
on tree trunks, reaching a height of 5 to 6 meters. Leaves are oblong-ovate,
up to 60 centimeters long, pinnately cleft almost to the midrib into 7 to 12
pairs of lanceolate, acuminate, falcate, 1-nerved lobes, 12 to 20 centimeters long,
2 to 5 centimeters wide. Spathes are several, terminal, white or greenish,
in flower about 15 centimeters long and deciduous. Spadix is green, dense, cylindric,
nearly or as long as the spathe, 2 to 2.5 centimeters thick in flower, thicker in fruit. Fruit is a greenish berry with a few seeds embedded in an orange-red pulp.
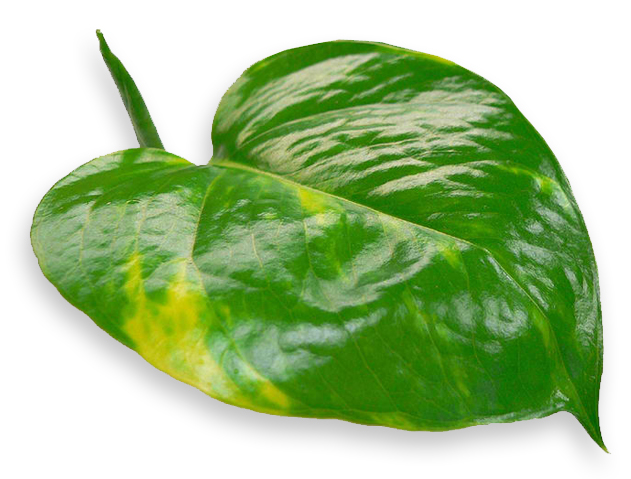
Epipremnum pinnatum is a large epiphytic aroid root-climber, scrambling up trees and rock surfaces with network of aerial clasping roots. Leaf morphology varies with physiological age of plant. Juvenile plants are terrestrial creepers. Plant produces mature leaves only when there is sufficient climbing height. Young leaves elliptical to arrow-shaped with entire margins. Mature leaves up to 30 - 50cm long, thick and leathery, ovate and pinnatifid (deeply incised along margins), often with white spots and pin-holes along mid-rib, and with fenestrations (windows) in leaf-blade -- superficially resembling Monstera species. Small (3-7mm across) on spathe-spadix inflorescences. Spathe (modified leaf) canoe-shaped, 10cm long, greenish on outside, creamy-white on inside; Monoecious species, spadix holds male and female flowers separately, white when fresh, maturing to creamy grey-green and then dark yellowish-green during anthesis, before air-drying to dark brown or almost black after anthesis. (11)
 Distribution Distribution
- Native to the Philippines.
-
In thickets and forests
at low and medium altitudes in Bontoc, Benguet, La Union, Nueva Viscaya, Zambales, Bataan, Rizal, Laguna, Quezon, and Sorsogon provinces in Luzon; Polilio, Palawan, Leyte, Negros and Mindanao.
- Urban ornamental cultivation.
- Also native to Andaman Is., Assam, Bangladesh, Bismarck Archipelago, Borneo, Cambodia, Caroline Is., China, Cook Is., Fiji, Hainan, India, Jawa, Laos, Lesser Sunda Is., Malaya, Maluku, Marshall Is., Myanmar, Nansei-shoto, New Caledonia, New Guinea, Nicobar Is., Northern Territory, Queensland, Samoa, Santa Cruz, Solomon Is., Sulawesi. Sumatera, Taiwan, Thailand, Tonga, Vanuatu, Vietnam, Wallis-Futuna Is.
(4)
Constituents
- Yields Benzenoid (11-phenyldecanoic acid, 15-phenylpen- tadecanoic acid, 13-phenyltridecanoic acid) and alkaloid (tongine). (6)
- Phytochemical screening of Rhaphidophora pinnata leaves yielded alkaloids, glycosides, saponins, flavonoids, tannins, and triterpenoids/steroid compound. (see study below)
(10)
- Bioactive-guided fractionation of leaves using expression of PTGS2 (COX2) mRNA isolated two C13 megastigmane glycosides, gusanlungionoside C (1) and citroside A (3), and the phenylalcohol glycoside phenylmethyl-2-O-(6-O-rhamnosyl)-ß-D-galactopyranoside (2), along with six additional megastigmane glycosides and aglycones ß-damascenone (10), megastigmatrienone (11), 3-hydroxy-ß-damascenone (12), and 3-oxo-7.8-dihydro-α-ionol (13). (see study below) (17)
Toxicity
- Epipremnum pinnatum contains calcium oxalate crystals that are toxic to both humans and pets. Ingestion by pets can cause vomiting, loss of appetite, drooling and pawing at the mouth. In humans, it can also cause burning or swelling around the mouth, general skin irritation, and contact dermatitis. All species in the genus Epipremnum share in toxicity potential. A case of toxic keratitis have been reported with Epipremnum aureum (Golden pothos).
Properties
- Emmenagogue, antidotal, anticancer.
- Leaves considered tonic and antirheumatic.
- Studies have suggested anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial properties.
Parts
utilized
Sap, leaves.
 Uses Uses
Folkloric
• Sap used for snake bites.
• Stem used as toothbrush to improve the breath.
• Spadix of plant used as emmenagogue.
• Leaves used for chest pains.
• Root, stem and leaf sheath chewed to alleviate dental ailments, also used for its soothing, sedating effect.
• Used for treatment of diabetes, cancer, and immune system enhancement.
• In Fiji, bark used as treatment of rheumatism, neuralgic headache, back pain, and muscular spasm.
• In Taiwan, used as dental analgesic.
• Mixture of young leaves of E. pinnatum and Imperata cylindrica is crushed in water or coconut juice and solution drunk to treat gonorrhea. Young leaves boiled in water used to treat diabetes and malaria; also used for toothaches. Juice extracted from stem mixed with water and drunk for joint paints, dislocation, and fractures. (6)
• In Chinese medicine, used for rheumatism, dysentery and fractures.
• Decoction of leaves used for treatment of malaria.
• Stem juice mixed with water and drunk for joint problems, fractures, and dislocations.
• Decoction of leaves use as gargle and mouth wash for gum inflammations
and tooth abscesses.
• In Malaysia and Singapore, Epipremnum pinnatum has a reputation as anticancer preparation and a remedy for skin diseases.
• In Fiji, stem considered to have contraceptive properties while the liquid expressed from the stem is used to regulate menstruation and promote fertility. (13)
• In India, bark used for wound healing. (16)
Others
• Teeth-blackening: Vine used by some Mindanao tribes, also in Bali, Java and Taiwan, used as a chewing agent for teeth blackening. (3)
• Basketry: Inner part or central cylinder of root used for basketry, lamp shades, etc.
Studies
• Anticancer / Apoptotic and Non-Apoptotic Mechanisms: Study of chloroform extract showed growth inhibition against T-47D breast carcinoma cells. Analysis of cell death mechanisms showed the extract elicited both apoptotic and non-apoptotic programmed cell deaths, possibly contributed to by up-regulation of caspase-3 and c-myc mRNA expression, respectively. (2)
• Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase: Study evaluated the an extract of E. pinnatum on pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity using Chicken pancreas model. Results showed lipase inhibition activity by 74% using 48 µg/ml of E. pinnatum extract. (7)
• Anticancer / Non-Apoptotic Cell Death: A hexane extract of E. pinnatum produced significant growth inhibition against T-47D breast carcinoma. Analysis of cell death mechanisms indicated the extract elicited a non-apoptotic programmed cell death. The up-regulation of c-myc mRNA expression may have contributed to the growth arrest and type II non-apoptotic programmed cell death in the extract treated T-47D cells. (8)
• Anti-Inflammatory / COX-2 Inhibition: Cox-2 is a mediator of inflammation and is highly expressed in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, asthma and various autoimmune disorders. Study evaluated various leaf extracts of E. pinnatum on COX-2 gene expression. Results showed a methanol extract exhibited strong COX-2 gene expression inhibition in-vitro. (9)
• Antibacterial / Leaves: Study evaluated ethyl acetate and ethanols extracts of Rhaphidophora pinnata leaves against Streptococcus mutans, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhi, and Shigella dysenteriae bacteria. The ethanol extract showed satisfactory activity against P. aeruginosa. The EA extract showed satisfactory activity against four types of bacteria. (see constituents above) (10)
• Anti-Inflammatory / Analgesic / Toxicity Study / Aerial Parts: Study evaluated ethanol extracts of aerial parts of R. pertusa and Epipremnum pinnatum for anti-inflammatory activity in Wistar albino rats and analgesic effects in Swiss albino mice. Both showed significant inhibition of carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats and significant inhibition of acetic acid-induced writhing in mice. In toxicity study, no mortality occurred within 24 hours of 3 doses of RP and EP (125, 250, and 500 mg/kg). The LD50 of both extracts was greater than 500 mg/kg p.o. in mice. (12)
• Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase Activity: Study of E. pinnatum extract using chicken pancreas showed 75% inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity. (14)
• COX-2 mRNA Inhibition: Study of E. pinnatum displayed promising COX-2 mRNA inhibition at 20 g/ml. Study yielded citroside A, qusanlungionoside C, and phenylmethyl-2-O-(6-O-rhamnosyl)-ß-D-galactopyranoside. One of the glycons, -damascenone, showed promising COX-2 mRNA inhibition (IC50=25.8 M). -Damascenone was not cytotoxic up to 50M. Results suggest -damascenone anti-inflammatory effect is expressed by targeting NF-B. (15)
• Megastigmane Derivatives / ß-Damascenone / Anti-Inflammatory / Leaves: Study evaluated leaf extracts of E. pinnatum for ability to inhibit inflammatory gene expression in endothelial- and monocyte-like cells (HUVECtert and THP-1, respectively). Bioactive-guided fractionation isolated two C13 megastigmane glycosides, gusanlungionoside C (1) and citroside A (3), and the phenylalcohol glycoside phenylmethyl-2-O-(6-O-rhamnosyl)-ß-D-galactopyranoside (2), along with six additional megastigmane glycosides and aglycones ß-damascenone (10), megastigmatrienone (11), 3-hydroxy-ß-damascenone (12), and 3-oxo-7.8-dihydro-α-ionol (13). Compound 10 (ß-damascenone) inhibited LPS-stimulated induction of mRNAs encoding for proinflammatory cytokines and leukocyte adhesion molelcules. Compound 10 also inhibited upregulation of inflammatory proteins and inhibited NF-kB dependent transcription. Study suggests the inhibition of NF-kB by ß-damascenone (10) may be one of the mechanisms underlying the in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of E. pinnatum extracts. (17)
• Hypoglycemic / Leaves: Study evaluated the hypoglycemic property of Tibatib leaf extract on alloxan-induced Sprague Dawley rats. Extract was administered by oral gavage. Results showed the leaf extract can lower blood glucose levels as effectively as positive control metformin. (18)
Availability
- Wildcrafted.
- Ornamental cultivation.
|



 Botany
Botany
 Uses
Uses

